
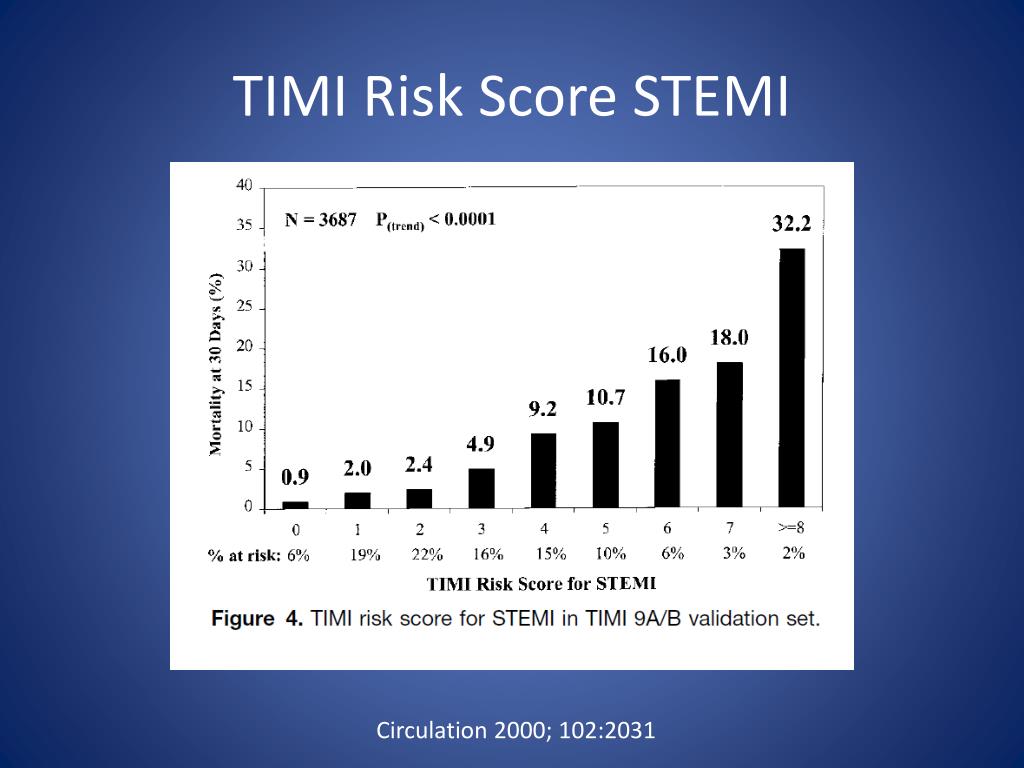
Morrow DA, Antman EM, Snapinn SM et al (2002) An integrated clinical approach to predicting the benefit of tirofiban in non-ST elevation acute coronary syndromes. Sabatine MS, McCabe CH, Morrow DA et al (2002) Identification of patients at high risk for death and cardiac ischemic events after hospital discharge. JAMA 284:835–842īudaj A, Yusuf S, Mehta SR et al (2002) Benefit of clopidogrel in patients with acute coronary syndromes without ST-segment elevation in various risk groups. ConclusionĪ modified TIMI risk score may simplify risk stratification of ED patients with undifferentiated chest pain.Īntman EM, Cohen M, Bernink PJ et al (2000) The TIMI risk score for unstable angina/non-ST elevation MI: a method for prognostication and therapeutic decision making. A simplified TIMI risk score was computed and was found to have similar prognostic ability as the 7 variable TIMI risk score. Four of the 7 TIMI risk factors (age ≥65 years, ST segment deviation ≥0.5 mm elevated troponin I, and coronary stenosis ≥50%) were independently associated with adverse events. The mean TIMI risk score was significantly higher in patients with an adverse event compared with those without (2.6 ± 1.3 vs. At 30 days there were 48 (5%) deaths, 84 (9%) myocardial infarctions, and 49 (5%) coronary revascularization procedures. There were 151 (16%) patients diagnosed with ACS. A multivariate analysis was done to evaluate the independent predictive power of the individual components of the TIMI risk score to predict an adverse event at 30 days (all-cause death, myocardial infarction, and coronary revascularization). We investigated the prognostic utility of the TIMI risk score in 947 consecutive patients evaluated in the ED for possible ACS.

The ability of the TIMI risk score to risk stratify patients at initial presentation in the ED with chest pain of unclear etiology is uncertain. Observed differences in performance may be due to incorporation bias.To assess the prognostic utility of the Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction (TIMI) risk score in patients in the emergency department (ED) evaluated for possible acute coronary syndrome (ACS). Area under the receiver operating characteristic curve for the composite outcome was 0.80 (0.76 to 0.83) for the mTIMI score compared with 0.71 (0.67 to 0.74) for the standard TIMI score, p0 to allow safe and early discharge without further investigation or follow-up. Of the 1666 patients, 219 (13%) reached the study outcome. The study outcome was a composite of all-cause death, myocardial infarction or coronary revascularisation within 30 days. We aimed to evaluate the performance of the mTIMI score in ED patients with suspected ACS.Ī multicentre prospective observational study enrolled patients undergoing assessment for possible ACS. A modified TIMI score (mTIMI, range 0-10), which gives increased weighting to these variables, has been proposed. The Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction (TIMI) risk score (range 0-7), used for emergency department (ED) risk stratification of patients with suspected acute coronary syndrome (ACS), underestimates risk associated with ECG changes or cardiac troponin elevation.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
